Businesses looking for a deeper understanding of their profitability have a variety of financial metrics to choose from, and which one they focus on depends on what insights the business is hoping to glean. Operating profit margin is a crucial profitability measure because it gives a good idea of the sustainability and scalability of a company’s core business model, potentially guiding decision makers on how to improve the efficiency of their operations and build on their strengths for the long term.
Operating Profit Margin Explained
Operating profit margin is often called one of the most important measures of a company. It includes all of a business’s operating costs: the direct costs of producing items or services for sale – known as cost of goods sold (COGS) – and indirect costs of operations, like sales, marketing, corporate salaries, professional fees, office rent, and utilities. Most recurring and regular business expenses are accounted for when calculating operating profit margin. Ancillary, nonrecurring losses and gains, like the sale of old equipment and investment gains or losses, are typically not included, nor are taxes or interest expense.
Operating profit margin occupies a sort of “Goldilocks” zone between gross profit and net profit because it holistically measures profitability of the core business processes without the potential ambiguity that nonoperating activity can create. Whereas gross profit margin includes only the direct costs to produce a good, operating expenses add in the indirect and overhead costs necessary to run the business, from administrative payroll to shipping the product to providing customer service. Thus, the operating margin gives managers and outside stakeholders a more complete picture of the profitability – and long-term viability – of the core business. External stakeholders, like investors and lenders, consider operating profit a reliable measure of a company’s earnings “quality” because it reveals more than gross profit while excluding atypical and one-off events like lawsuit settlements or large investment gains and losses, which sometimes influence net profit margin.
Operating Profit Margin Formula
Operating profit margin can be calculated with this simple formula:
Operating Profit Margin = Total Revenue – ( Cost of Goods Sold + Operating Expenses ) x 100
Total Revenue
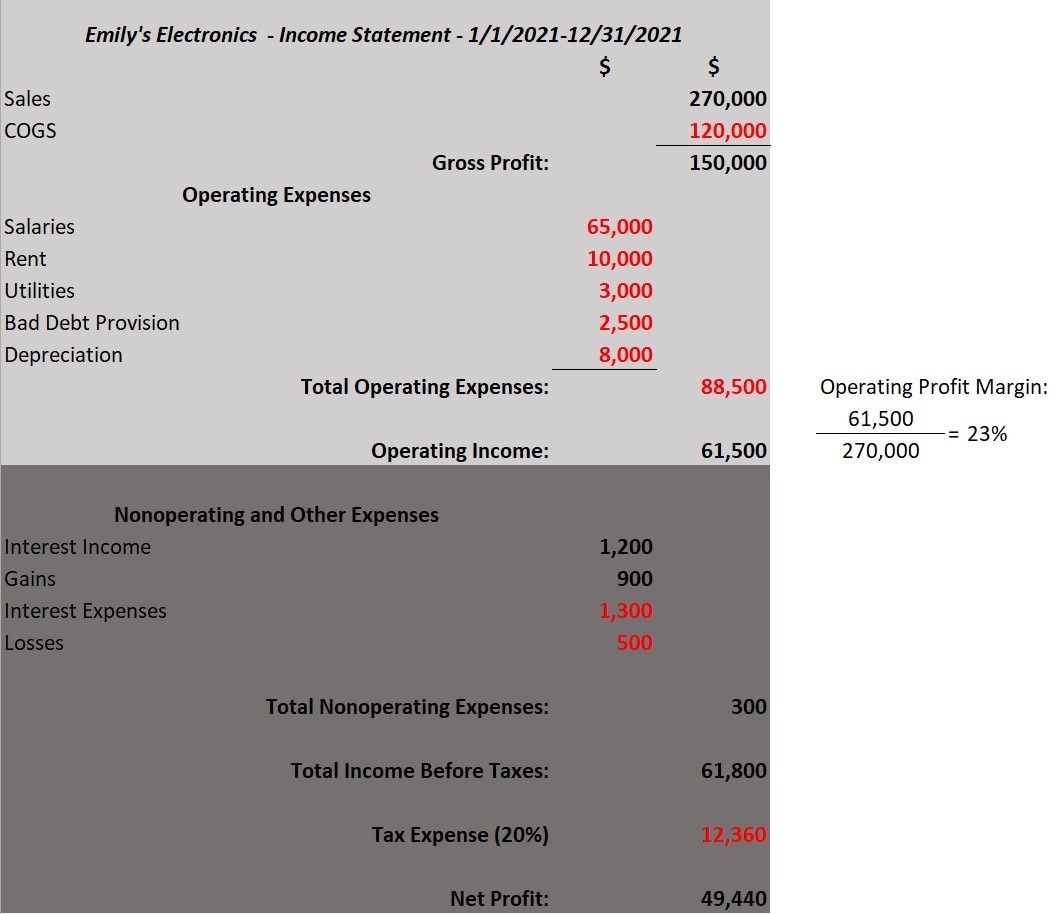
A typical company income statement is structured so that the top section shows total revenue, COGs, and gross profit, with operating expenses listed after that, as shown below in a hypothetical income statement for the fictional Emily’s Electronics. Total operating income – which is what’s left after subtracting COGS and operating expenses from revenue – shows the profitability of a business’s core operations.
Emily’s Electronics’ sample income statement below shows annual revenue of $270,000 and $120,000 in COGS, leaving a gross profit of $150,000. Reading down the statement, operating expenses, including rent and salaries, are shown, for a sum of $88,500. Subtracting those operating expenses from the gross profit leaves the business with $61,500 in operating income, or profit, that it can use for reinvestment, expansion, or miscellaneous nonoperating expenses. Dividing that $61,500 by the revenue of $270,000 and multiplying by 100 gives an operating profit margin of approximately 22.8%. The shaded section of the income statement shows Emily’s Electronics’ nonoperating and miscellaneous gains and losses, which are not considered when calculating operating income but do affect net income.
How Managers, Analysts, and Investors Use Operating Profit Margin
For small-business owners and senior managers, operating profit margin is a way to assess their overall business model. Does it make a profit after all costs are factored in (direct and indirect)? Is it sustainable – or did we only make a profit this quarter because we have four unfilled staff positions? Is it scalable – in other words, can our indirect costs handle more sales volume and still generate profit?
By producing income statements monthly, quarterly, or yearly, business managers can review their operating margin to get a sense of how profitability and productivity are changing over time. If a business shows a strong operating margin, it’s a good sign that managers can expand operations – perhaps by hiring more sales staff or increasing distribution and marketing – and still remain profitable.
Operating margins are also valuable forecasting tools because they capture most of a business’s recurring costs and contextualize those costs in relation to revenue.
Operating margins are also valuable forecasting tools because they capture most of a business’s recurring costs and contextualize those costs in relation to revenue. This helps businesses make more accurate cost projections. While regularly running these reports may be time-consuming, many modern companies automate the reports to keep the data up to date and readily available, with minimal effort and expense.
Moreover, operating margins let a business see how efficiently it's operating by comparing its margin with that of other companies in the industry. There is no standard “good” operating profit margin. Some businesses, like grocery stores, tend to naturally have thinner margins, while others have fatter margins. But unlike gross profit margins, which only include revenue and COGS, operating profit margins can help reveal how effectively managed a company is. That's because decision makers typically have more control over allocation of funds for operating costs, like salaries and corporate offices, than they do for manufacturing costs, which tend to be more tied to external factors, like the cost of raw materials.
What Operating Profit Margin Can’t Tell You
As important as operating profit margin is, it doesn't take into account how one's products and services stack up in the current market. For example, even if a business has high margins from strong sales, it may still have an opportunity to increase margins by raising prices – without having to alter any operations.
Also, operating margin doesn’t represent cash flow – often a major factor in company’s financial health. Profits are typically calculated when a sale is earned, but many businesses experience a lag between when a sale is made and when an invoice is paid. Such lag times in accounts receivable collections can mean that a business has high profit margins, but is nonetheless unable to pay its bills on time.
The Takeaway
Operating profit margin reflects the results of a company’s core business. It is the amount of profit after considering direct costs of goods sold and indirect costs of running the business, such as selling, general and administrative expenses, marketing, overhead, and depreciation. Thus, operating margin is a useful ratio for evaluating not only the health of the business but also how efficiently it is managed.
Photo: Getty Images

